SIP Cable: Unveiling Resilience in Electrical Transmission
Understanding SIP Cable: Decoding Its Significance
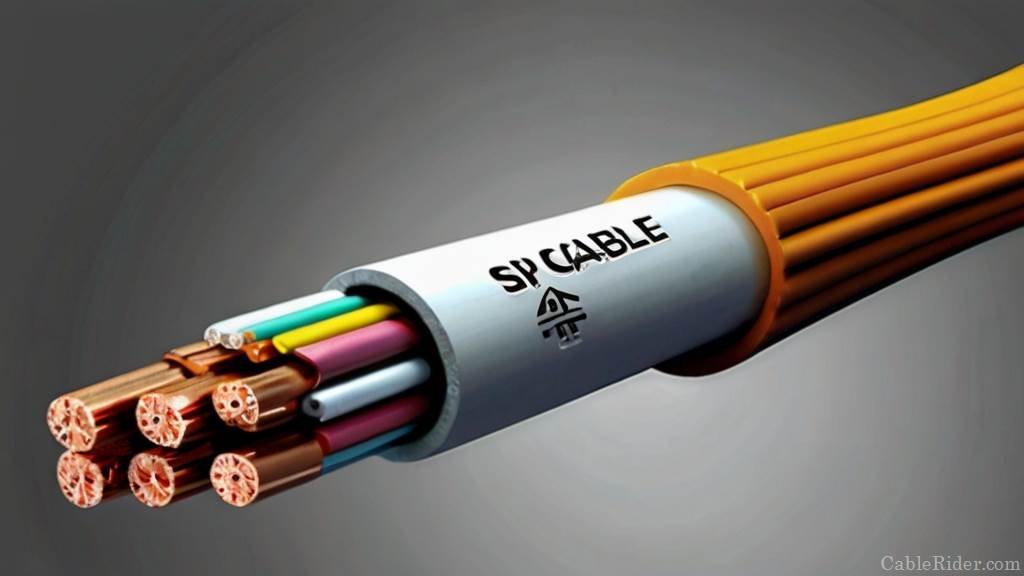
Deciphering SIP: Self-Supporting Insulated Wire
SIP cable, short for Self-Supporting Insulated Wire, is a vital component in electrical systems, playing a crucial role in ensuring efficient transmission of electricity. But what exactly makes SIP cable stand out in the realm of electrical wiring?
Contents
ToggleSelf-supporting insulated wire refers to a type of cable designed with insulation material to prevent electrical leakage and ensure safety. Unlike conventional cables that require additional support structures like poles or towers for installation, SIP wire boasts inherent strength, allowing it to be suspended between points without the need for external support.
This innovative design not only simplifies installation but also minimizes the need for maintenance, making it a cost-effective solution for various applications. But how does SIP wire achieve such versatility and reliability?
Exploring SIP Wire: Its Composition and Functionality
SIP cable typically consists of several layers, each serving a specific purpose to enhance its performance. The core of SIP wire is typically made of conductive material, such as copper or aluminum, to facilitate the flow of electricity. Surrounding the core is an insulating layer, usually composed of materials like PVC or polyethylene, which prevents electrical currents from escaping and protects against external factors like moisture and corrosion.
One of the distinguishing features of SIP cable is its self-supporting design, achieved through the incorporation of additional strengthening elements within the cable structure. These may include embedded steel strands or aramid fibers, providing the necessary tensile strength to support the weight of the cable over long spans.
In addition to its robust construction, SIP wire is also engineered to meet specific performance requirements, such as temperature resistance and signal integrity. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from telecommunications networks to overhead power distribution lines.
SIP Cable vs. Conventional Cable: A Comparative Analysis
When comparing SIP cable to conventional cable designs, several key differences emerge that highlight the unique advantages of SIP wire. Unlike traditional cables that rely on external support structures, SIP cable offers greater flexibility in installation, allowing for quicker deployment and reduced labor costs.
Moreover, the self-supporting nature of SIP wire eliminates the need for additional hardware, such as insulators and brackets, further streamlining the installation process. This not only saves time but also reduces the environmental impact associated with manufacturing and disposing of excess materials.
Another significant advantage of SIP cable is its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, thanks to its durable construction and weather-resistant insulation. Whether facing extreme temperatures, high winds, or heavy precipitation, SIP wire remains reliable and resilient, ensuring uninterrupted power transmission.
In conclusion, SIP cable represents a significant advancement in electrical wiring technology, offering unparalleled versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding its composition, functionality, and comparative advantages, we can fully appreciate the significance of SIP wire in modern electrical systems.
So, what do you think about SIP cable’s unique design and benefits? How do you envision its role in shaping the future of electrical infrastructure? Share your thoughts below!
Delving into the Mechanics: What is SIP in Electrics?
SIP in Electrics: An Overview of its Application
SIP, standing for Self-Supporting Insulated Wire, is a game-changer in the field of electrical engineering. But how exactly does SIP find its application in the vast landscape of electrical systems?
In its simplest form, SIP wire is utilized in various electrical installations where traditional cables face limitations. Its self-supporting nature makes it ideal for overhead applications, eliminating the need for additional support structures like poles or towers. This makes SIP wire a preferred choice in scenarios where space constraints or terrain challenges make traditional installations impractical.
The Evolution of SIP Cable in Electrical Engineering
The journey of SIP cable in electrical engineering is nothing short of remarkable. From its humble beginnings to its current state-of-the-art designs, SIP wire has undergone significant evolution to meet the ever-growing demands of modern infrastructure.
Initially developed as a solution to simplify overhead wiring installations, SIP cable has evolved to encompass a wide range of applications across different industries. Advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes have contributed to the development of SIP wire variants tailored to specific performance requirements, such as high-voltage transmission or telecommunications.
SIP Cable Decoding: Unraveling its Technical Specifications
Deciphering the technical specifications of SIP cable is essential to understanding its capabilities and limitations. Let’s dive into the key components that make up SIP wire and how they contribute to its overall performance.
Core Material:
At the heart of SIP cable lies its conductive core, typically made of materials like copper or aluminum. This core facilitates the flow of electrical current, ensuring efficient transmission from source to destination.
Insulation:
Surrounding the core is an insulating layer, designed to prevent electrical leakage and protect against external factors like moisture and corrosion. Materials such as PVC or polyethylene are commonly used for insulation, offering excellent dielectric properties and durability.
Strength Members:
One of the defining features of SIP cable is its self-supporting design, achieved through the incorporation of additional strengthening elements within the cable structure. These may include embedded steel strands or aramid fibers, providing the necessary tensile strength to support the weight of the cable over long spans.
Weather Resistance:
SIP wire is engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions, thanks to its weather-resistant insulation and robust construction. Whether facing extreme temperatures, high winds, or heavy precipitation, SIP cable remains reliable and resilient, ensuring uninterrupted power transmission.
In conclusion, SIP cable represents a significant advancement in electrical wiring technology, offering unparalleled versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding its application, evolution, and technical specifications, we can fully appreciate the role of SIP wire in shaping the future of electrical infrastructure.
So, what are your thoughts on SIP cable’s journey and technical specifications? How do you envision its continued evolution in the years to come? Share your insights below!
Unveiling the Vulture: Exploring the Concept
What is Vulture in Electrical Engineering?
Vulture, in the realm of electrical engineering, isn’t the soaring bird we typically associate with the term. Instead, it refers to a crucial element within SIP cable technology that plays a significant role in enhancing its performance. But what exactly is this vulture, and how does it contribute to the functionality of SIP wire?
In simple terms, vulture refers to the central strength member within SIP cable, responsible for providing structural support and stability. Much like the sturdy backbone of a creature, the vulture in SIP cable serves as the backbone of the entire system, ensuring its integrity and reliability.
Significance of Vulture in SIP Cable Technology
The presence of vulture in SIP cable technology is paramount, offering several key advantages that set it apart from conventional wiring solutions. One of the primary benefits is its ability to support the weight of the cable over long spans without the need for additional support structures.
This inherent strength not only simplifies installation but also reduces the overall cost and complexity of the electrical infrastructure. Additionally, vulture enhances the durability and resilience of SIP wire, making it suitable for use in diverse environments and applications.
Vulture in SIP Cable: Its Role in Enhancing Performance
The role of vulture in SIP cable goes beyond mere structural support. It also contributes to the overall performance and efficiency of the electrical system. By providing a stable platform for the transmission of electrical currents, vulture helps minimize signal loss and ensures consistent power delivery.
Moreover, the presence of vulture enables SIP cable to withstand external factors such as wind, ice, and temperature fluctuations, further enhancing its reliability and longevity. This makes SIP wire with vulture an ideal choice for outdoor installations, including overhead power lines and telecommunications networks.
In essence, vulture serves as the backbone of SIP cable technology, providing the necessary strength and stability for efficient power transmission. Its significance cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in ensuring the reliability and resilience of electrical infrastructure.
So, what are your thoughts on the concept of vulture in SIP cable technology? How do you envision its role evolving in the future of electrical engineering? Share your insights below!
SIP Cable: Exploring Its Diverse Applications
Industrial Applications of SIP Cable
SIP cable finds extensive use in various industrial settings, where reliability, efficiency, and durability are paramount. From manufacturing facilities to heavy machinery installations, SIP wire plays a crucial role in ensuring uninterrupted power supply and smooth operation.
In industrial environments, where machinery operates round the clock, SIP cable’s robust construction and weather-resistant properties make it an ideal choice for overhead power distribution. Its self-supporting design eliminates the need for additional support structures, simplifying installation and reducing maintenance costs.
Moreover, SIP cable’s ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures and chemical exposure, makes it well-suited for use in demanding industrial applications. Whether it’s powering conveyor systems in a factory or providing electricity to remote equipment in a mining operation, SIP wire proves to be a reliable and cost-effective solution.
Residential Usage of SIP Wire: A Practical Perspective
In residential settings, SIP wire offers homeowners a practical and efficient solution for electrical installations. From powering lighting fixtures to supplying electricity to appliances, SIP cable finds diverse applications within the home.
One of the key advantages of SIP wire in residential settings is its versatility and ease of installation. Its self-supporting design allows for hassle-free deployment, whether it’s running wiring along rooftops or through tight spaces within the walls.
Furthermore, SIP cable’s insulation properties ensure safety and reliability, protecting against electrical hazards and minimizing the risk of fire. This makes it a preferred choice for homeowners looking to upgrade their electrical systems or undertake new construction projects.
Innovations in SIP Cable Technology: Paving the Way Forward
As technology continues to advance, so too does the evolution of SIP cable. Innovations in materials science, manufacturing processes, and design principles are paving the way for enhanced performance and functionality.
One notable innovation is the development of high-voltage SIP cable variants capable of transmitting electricity over long distances with minimal signal loss. These advancements open up new possibilities for renewable energy integration, grid modernization, and electrification initiatives.
Moreover, ongoing research in areas such as nanotechnology and smart materials holds the promise of further improving the efficiency and reliability of SIP wire. From self-healing insulation to sensors embedded within the cable structure, future innovations are poised to revolutionize the way we think about electrical wiring.
In conclusion, SIP cable’s diverse applications span across industrial, residential, and emerging technology sectors. Its reliability, efficiency, and adaptability make it a cornerstone of modern electrical infrastructure, driving innovation and progress in the field.
What are your thoughts on the diverse applications of SIP cable? How do you envision its role evolving in the ever-changing landscape of electrical engineering? Share your insights below!
SIP Cable in the Modern Era: Understanding Its Relevance
Adapting to the Future: SIP Cable in Smart Grids
As we stride into the digital age, the concept of smart grids has emerged as a transformative solution for optimizing energy distribution and consumption. SIP cable plays a pivotal role in this transition, offering a reliable and efficient means of transmitting electricity within these advanced grid systems.
Smart grids leverage advanced communication and control technologies to monitor and manage energy flow in real-time, enabling utilities to respond dynamically to changing demand and supply conditions. SIP wire, with its robust construction and high-performance capabilities, provides the backbone for these intelligent grid networks.
By integrating SIP cable into smart grid infrastructure, utilities can enhance grid reliability, improve energy efficiency, and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. This ensures a more resilient and sustainable energy ecosystem that meets the evolving needs of modern society.
SIP Cable in Renewable Energy Systems: A Sustainable Approach
The shift towards renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, has gained significant momentum in recent years as the world seeks to mitigate climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. SIP cable plays a crucial role in enabling the transmission of renewable energy from generation sources to end-users.
In renewable energy systems, SIP wire facilitates the efficient and reliable transmission of electricity over long distances, connecting remote wind farms and solar arrays to the wider power grid. Its self-supporting design and weather-resistant properties make it well-suited for outdoor installations, where exposure to the elements is inevitable.
Furthermore, SIP cable contributes to the overall sustainability of renewable energy systems by minimizing energy losses during transmission, thereby maximizing the efficiency of clean energy generation. This underscores its importance in advancing the transition towards a greener and more sustainable future.
SIP Wire in Telecommunications: Ensuring Connectivity
In an increasingly interconnected world, reliable telecommunications infrastructure is essential for facilitating communication and connectivity. SIP wire plays a critical role in supporting telecommunications networks, ensuring the seamless transmission of voice, data, and video signals.
Whether it’s providing backbone connectivity for fiber optic cables or supporting overhead telephone lines, SIP cable offers a versatile and dependable solution for telecommunications infrastructure. Its self-supporting design and high-performance characteristics make it ideal for spanning long distances and navigating challenging terrain.
Moreover, SIP wire’s insulation properties and resistance to electromagnetic interference help maintain signal integrity and reliability, ensuring consistent connectivity even in the face of external disturbances.
In conclusion, SIP cable remains highly relevant in the modern era, with applications spanning smart grids, renewable energy systems, and telecommunications infrastructure. Its reliability, efficiency, and versatility make it an indispensable component of our increasingly interconnected world.
What are your thoughts on the relevance of SIP cable in today’s technological landscape? How do you see its role evolving in the future? Share your insights below!
SIP Cable Installation and Maintenance: Best Practices
Installing SIP Cable: Guidelines and Considerations
Installing SIP cable requires careful planning and adherence to specific guidelines to ensure a safe and reliable electrical infrastructure. Here are some best practices to consider:
-
Site Assessment: Before installation, conduct a thorough assessment of the site to identify any potential obstacles or hazards that may impact the installation process.
-
Proper Support Structures: Ensure that adequate support structures are in place to accommodate the weight of the SIP cable. This may include poles, towers, or other support mechanisms, depending on the installation location and requirements.
-
Correct Installation Techniques: Follow manufacturer guidelines and industry standards for the proper installation of SIP cable. This includes techniques for securing the cable, maintaining proper tension, and ensuring adequate clearance from surrounding objects.
-
Weather Considerations: Take into account weather conditions during installation, as adverse weather can affect the safety and efficiency of the installation process. Schedule installations during favorable weather conditions whenever possible.
-
Quality Assurance: Conduct quality checks throughout the installation process to ensure that the SIP cable is installed correctly and meets performance standards. This may include testing for continuity, insulation resistance, and mechanical integrity.
Maintenance Strategies for SIP Wire: Ensuring Longevity
Regular maintenance is essential for preserving the integrity and performance of SIP wire over time. Here are some maintenance strategies to help ensure longevity:
-
Scheduled Inspections: Implement a schedule for routine inspections of SIP cable installations to identify any signs of wear, damage, or deterioration. Inspections should include visual checks as well as testing for electrical continuity and insulation resistance.
-
Preventive Maintenance: Take proactive measures to address potential issues before they escalate into larger problems. This may include cleaning, lubricating, and tightening connections, as well as replacing worn or damaged components.
-
Environmental Considerations: Consider the environmental conditions surrounding the SIP cable installation and take appropriate measures to protect against factors such as moisture, temperature extremes, and exposure to chemicals or pollutants.
-
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities, including inspection reports, repair records, and any modifications made to the SIP cable installation. This documentation can help track maintenance history and identify recurring issues.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with SIP Cable
Despite careful installation and maintenance, SIP cable installations may encounter issues from time to time. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
-
Intermittent Connectivity: If experiencing intermittent connectivity issues, check for loose or damaged connections, corrosion, or interference from nearby electrical or electronic devices.
-
Insulation Damage: Inspect the SIP cable for signs of insulation damage, such as cuts, abrasions, or exposed conductors. Address any damage promptly to prevent further deterioration and ensure electrical safety.
-
Mechanical Stress: Assess the SIP cable for signs of mechanical stress, such as kinks, twists, or excessive tension. These issues can compromise the structural integrity of the cable and may require adjustments or reinforcement.
-
Environmental Factors: Consider environmental factors that may impact SIP cable performance, such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, or exposure to chemicals. Take appropriate measures to mitigate these factors and protect the cable from damage.
By following these best practices for SIP cable installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, you can ensure the longevity and reliability of your electrical infrastructure. Remember to prioritize safety and adherence to industry standards throughout the process to minimize risks and maximize performance.
What are your experiences with SIP cable installation and maintenance? Do you have any additional tips or insights to share? Let us know in the comments below!
Exploring Cable SIB: Understanding the Relationship with SIP
Cable SIB vs. SIP Cable: Distinguishing Features
When delving into the realm of electrical wiring, it’s essential to understand the nuances between Cable SIB and SIP cable. While both serve similar functions in electrical systems, they possess distinct characteristics that set them apart.
Cable SIB, or Self-Insulating Braid, is a type of wiring commonly used in electrical applications where insulation is crucial. Unlike conventional cables, which require additional insulation materials, Cable SIB features an integrated insulating braid that provides protection against electrical leakage and external factors.
On the other hand, SIP cable, or Self-Supporting Insulated Wire, is renowned for its self-supporting design, eliminating the need for external support structures. SIP wire is often used in overhead installations where space constraints or terrain challenges make traditional wiring methods impractical.
While both Cable SIB and SIP cable offer unique advantages in their respective applications, it’s essential to consider factors such as installation requirements, environmental conditions, and performance specifications when choosing between the two.
Integration of Cable SIB and SIP Wire in Electrical Systems
In modern electrical systems, the integration of Cable SIB and SIP wire offers a synergistic approach to addressing diverse infrastructure needs. By combining the insulation properties of Cable SIB with the self-supporting design of SIP cable, engineers can create robust and resilient electrical networks capable of withstanding various challenges.
For example, in outdoor installations where exposure to harsh weather conditions is a concern, integrating Cable SIB with SIP wire provides an added layer of protection against moisture, temperature extremes, and environmental contaminants. This ensures the longevity and reliability of the electrical infrastructure, minimizing the risk of downtime or performance issues.
Moreover, the integration of Cable SIB and SIP cable allows for greater flexibility and adaptability in designing electrical systems tailored to specific requirements. Whether it’s powering telecommunications networks, industrial machinery, or residential buildings, the combined capabilities of Cable SIB and SIP wire offer endless possibilities for innovation and optimization.
Future Prospects: Enhancing Synergy between Cable SIB and SIP Cable
As technology continues to evolve, the future prospects for Cable SIB and SIP cable look promising. Advances in materials science, manufacturing techniques, and design methodologies are paving the way for enhanced synergy between these two wiring solutions.
One potential area of development is the optimization of Cable SIB and SIP wire for emerging applications, such as smart grids, renewable energy systems, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. By leveraging the unique properties of Cable SIB and SIP cable, engineers can create intelligent, interconnected electrical networks capable of meeting the evolving demands of modern society.
Furthermore, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving the performance, efficiency, and sustainability of Cable SIB and SIP wire. This includes exploring innovative insulation materials, enhancing self-supporting designs, and integrating smart technologies for real-time monitoring and control.
In conclusion, the relationship between Cable SIB and SIP cable holds tremendous potential for advancing the field of electrical engineering. By understanding their distinguishing features, exploring integration opportunities, and embracing future prospects, we can unlock new possibilities for creating safe, reliable, and resilient electrical systems.
What are your thoughts on the relationship between Cable SIB and SIP cable? How do you envision their role evolving in the future of electrical infrastructure? Share your insights below!


